In the world of Blockchain, we often face a paradox: All data is public, yet Smart Contracts are “blind” to their own history. While Smart Contracts excel at managing the current state, they are notoriously inefficient at accessing past data.
This is where Brevis steps in. Often described as the “key” to unlocking the blockchain black box, Brevis promises to bring Infinite ZK Compute capabilities to decentralized applications.
What is Brevis?
Brevis is a Smart ZK Coprocessor. It empowers Smart Contracts to read complete historical data across blockchains and perform custom computations in a completely decentralized (trust free) manner.
Unlike Layer 2 solutions that focus on scaling throughput or transaction speed, Brevis focuses on scaling data computation.
Current Smart Contracts face a significant limitation: they can only efficiently access current state. Retrieving historical data (e.g., transactions from 3 years ago) directly on chain is either impossible due to technical constraints or prohibitively expensive due to gas costs.
Learn more: Crypto Exchange – The Cornerstone of Crypto Market
Brevis resolves this bottleneck by:
- Historical Data Access: Allowing Smart Contracts to read data from any past block (transactions, events, states).
- Low Cost Computation: Offloading heavy computational tasks (such as aggregating trade volume or analyzing wallet behavior) away from the blockchain (off chain).
- Trust free Verification: Using ZK Proofs to mathematically prove the accuracy of calculation results, eliminating the need to trust third parties like Centralized Indexers or Oracles.
The strongest advantage of Brevis compared to older ZK solutions is its flexibility. It is not just a static ZK circuit. Developers can customize computational logic according to their dApp’s specific needs via SDK tools (notably the Pico Framework). This transforms Brevis into an open platform for all types of data applications.
What is Brevis? – Source Brevis
Brevis Architecture
To realize the vision of “infinite compute” while maintaining Ethereum level security, Brevis relies on an Asynchronous Architecture. This architecture completely decouples the computationally expensive execution from the low cost verification.
Below is an anatomical breakdown of the Brevis system and the lifecycle of a data request.
The Three Pillars of the Brevis System
The Brevis architecture is composed of three main layers:
- Interface Layer (SDK/API): Where developers define computational logic (Circuits) via code (such as Rust with Brevis Pico). This acts as the gateway between the dApp and the Brevis network.
- Prover Network (Off chain): The “Data Processing Factory.” This is a network of nodes responsible for retrieving historical data from source blockchains and generating ZK proofs.
- Verification Layer (On chain): Brevis Smart Contracts deployed on destination blockchains (Ethereum, BNB Chain, Base, etc.). The sole duty of this layer is to validate the authenticity of the ZK proofs.
Data Flow
To understand how the architecture operates, let’s follow the journey of a request from initiation to completion:
Step 1: Query Request – A user (or a dApp’s Smart Contract) sends a computation request.
Step 2: Processing at the Prover Network (The Heavy Lifting) – This is where the Brevis architecture shines. Nodes in the Brevis network perform two parallel tasks:
- Data Indexing: Retrieving precise Raw Data from block headers, state roots, transactions, or event logs of the source chain.
- Circuit Execution & Proving: The node runs the computational logic requested by the dApp on that data. Once the result is obtained, it generates a ZK Proof (Zero Knowledge Proof) – a cryptographic string confirming: “I have correctly calculated according to the requested logic on actual blockchain data.”
Step 3: On chain Submission & Verification – The Prover submits the computation result along with the ZK Proof to the Brevis Smart Contract on the destination chain.
- This contract acts as a “gatekeeper.” It uses ZK verification algorithms (such as Groth16 or Plonk) to check the proof.
- This process consumes very little gas, regardless of the volume of computation performed in Step 2.
Step 4: Callback and Execution – Upon successful verification, the Brevis system triggers a “Callback” function to send the Authenticated Result back to the original dApp’s Smart Contract.
At this point, the dApp can utilize this data (e.g., granting permission to mint a VIP NFT) with absolute trust (100% security guarantee), equivalent to the security of the underlying blockchain.
Co Chain Solutions Model
This is the most significant differentiator between Brevis and other ZK Coprocessors. Instead of forcing every transaction to generate an expensive ZK proof, Brevis offers a hybrid mechanism called Brevis Co Chain.
Co Chain Solutions Model – Source: Brevis
This model operates on an “Optimistic” mechanism combined with ZK security, functioning similarly to an AVS (Actively Validated Service) on EigenLayer.
Operational Mechanism:
- Propose (Fast Path): Upon request, Validators (secured by ETH restaking on EigenLayer) perform the calculation and return the result immediately. At this stage, no ZK Proof is generated.
- Challenge Window: The system opens a short waiting period. Anyone can verify this result.
- ZK Dispute Resolution: Normal Case (99%) – No challenges occur. The transaction finalizes with zero ZK costs. Fraud Case – If someone detects an incorrect result, they submit a challenge. Brevis then triggers the generation of a ZK Proof to act as the “judge.” If the Validator is wrong, they are penalized (Slashing).
Co Chain Mode, best for GameFi, SocialFi, or dApps requiring low latency and minimal costs. Thanks to the Optimistic mechanism, operational costs are significantly reduced as Proofs are not generated for every single transaction.
The Brevis architecture is not rigid. By flexibly combining Pure ZK and Co Chain (Optimistic ZK), Brevis allows developers to freely choose between “Absolute Security” and “Maximum Efficiency,” paving the way for ZK adoption in mass market applications.
Pico
If the Brevis architecture is the powerful “engine” under the hood, then Brevis Pico is the “steering wheel” that allows developers to control that power.
Previously, the biggest barrier preventing the explosion of ZK applications (ZK dApps) was not a lack of ideas, but the programming language. To build a ZK circuit, developers had to learn highly specialized and complex languages like Circom or Halo2, which demanded deep cryptographic knowledge. Brevis Pico was created to shatter that barrier.

Pico – Source: Brevis
ZK Blackbox
Pico’s core philosophy is the “ZK Blackbox.” It completely abstracts away the complexity of cryptographic proof generation.
- With legacy frameworks: You had to write code to instruct the computer how to generate mathematical proofs.
- With Pico: You simply write the application logic, and Pico automatically handles the underlying mathematics.
The Power of “Pure Rust”
Pico allows developers to use Rust the most beloved language in the blockchain space (utilized by Solana, Polkadot, Near, etc.) to write ZK smart contracts.
This offers immense advantages:
- Zero Learning Curve: Any Rust developer can become a Brevis ZK developer in a matter of hours.
- Access to the Ecosystem: You can leverage thousands of existing libraries (crates) from the Rust community directly within your ZK circuit. This capability was virtually impossible with older, domain specific ZK languages.
Consistency
Another significant pain point for ZK developers was inconsistency: The code used for testing logic often differed from the code used for actual circuit generation.
Pico solves this completely with Consistency. You write your computational logic once in Rust. That exact same code can run unit tests on your local machine and be compiled to execute on the Brevis Prover network.
Brevis Pico is not just a tool; it is the bridge bringing ZK technology from the research lab to the mass market. By combining the computational power of the Brevis architecture with the user friendliness of Rust, Pico is paving the way for a new wave of Web3 applications that are significantly more complex and intelligent.
Backers & Tokenomics
Based on on chain data and the latest disclosures, here is the detailed financial picture of the project.
Fundraising
Brevis established its “Blue chip” status right from its first funding round. In November 2024, the project announced the completion of its Seed Round, raising $7.5 Million.
- Binance Labs (YZi Labs): The venture arm of the world’s largest exchange. Binance Labs leading this round is a massive signal endorsing a potential future listing.
- Polychain Capital: A legendary Tier 1 fund known for incubating core blockchain infrastructure.
- Reputable Tier 2 Funds: IOSG Ventures, Nomad Capital, Bankless Ventures, HashKey Capital.
Tokenomics
The Brevis Total Supply is 1,000,000,000 (1 Billion) BREV and is a Fixed Supply. BREV is not just a governance token; it is the lifeblood running through the ZK Coprocessor network.
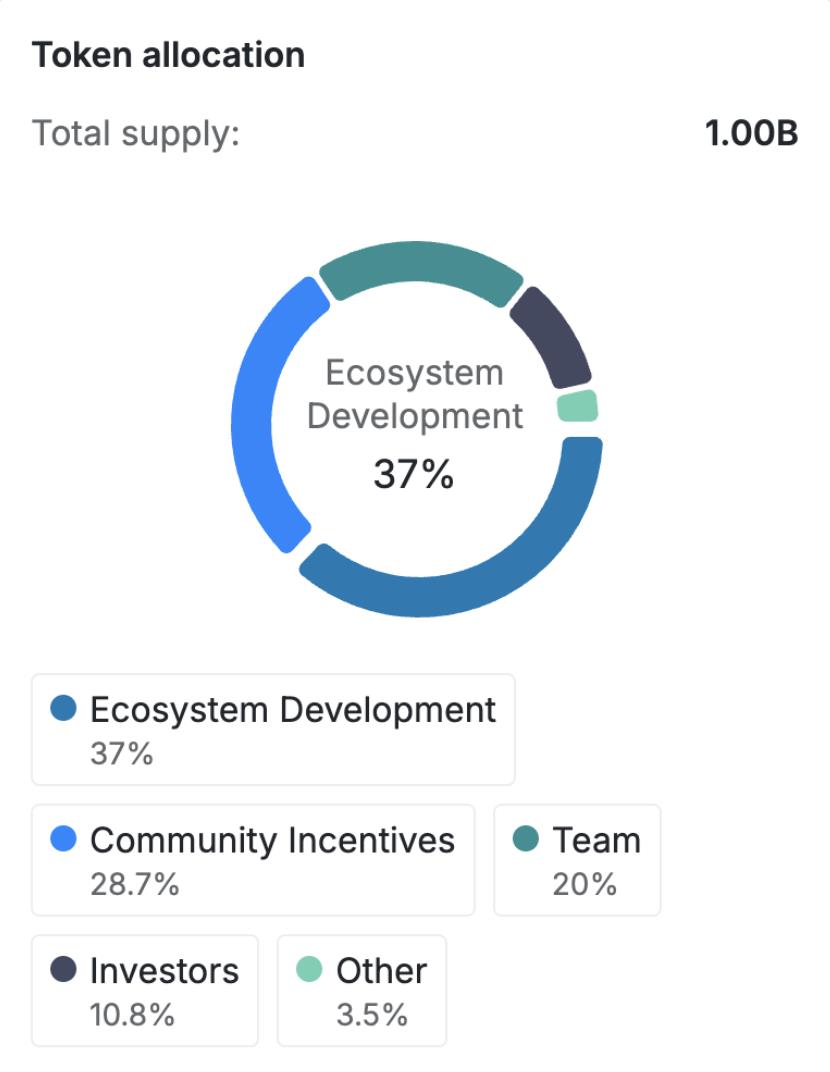
Tokenomics – Source: Brevis
The allocation structure demonstrates a strong focus on community and ecosystem growth:
- Ecosystem Development (37%):
- Community Incentives (28.7%)
- Team (20%)
- Investors (10.8%)
- Other (3.5%)

How to Buy BREV
Step 1: Prepare Account & USDT
- If you don’t have an account, register and complete Identity Verification (KYC) to the highest level to avoid deposit/withdrawal limits.
- Deposit USDT (Tether) or FDUSD into your Spot Wallet.
Step 2: Executing the Trade (Spot Trading)
- Navigate to Trade -> Spot.
- Search for the ticker: BREV.
- Select the corresponding trading pair: BREV/USDT (most common) or BREV/FDUSD.
Choose your Order Type:
- Limit Order (Recommended): Enter the specific price you want to pay (e.g., $0.50) and the amount. The order will only fill if the market price drops to your target.
- Market Order: Buys immediately at the current market price. Only use this if you see a strong pump and want to “FOMO” in.
Storage
- Short term (Trade): Keep BREV on the exchange wallet for easy profit taking.
- Long term (Hold): If you believe in the “Infinite Compute” vision and plan to hold for >1 year, withdraw your tokens to a Cold Wallet (Ledger, Trezor) or a personal Web3 Wallet
FAQ
What is Brevis?
Brevis is a Smart ZK Coprocessor. Think of it simply: If the Blockchain is the memory (storage), Brevis is the processor (computation). It enables Smart Contracts to access and process billions of historical data points securely and cost effectively, something that Ethereum or current L2s cannot efficiently do on their own.
How is Brevis different from The Graph?
The difference lies in the purpose. The Graph is an Indexing protocol, excellent at organizing data for display on website frontends. However, feeding that data back into a Smart Contract in a trustless manner is difficult and expensive. Brevis was created to solve this via Computation and Verification. Thanks to ZK technology, Brevis cryptographically proves the absolute accuracy of calculation results without needing human intervention or trust.
Is Brevis Co Chain secure if it doesn’t generate ZK Proofs for every transaction?
Yes, thanks to a multi layered security mechanism combining Economics and Mathematics. Validators in the Co Chain network must restake a significant amount of ETH via EigenLayer to ensure honesty. Additionally, a “Challenge” mechanism allows anyone to verify results; if fraud is detected, the system triggers a ZK Proof to act as the adjudicator. Malicious actors are slashed immediately, ensuring network safety.
Is using Brevis gas-expensive?
On the contrary, Brevis helps save significant Gas fees. Instead of forcing Smart Contracts to perform heavy computations directly on chain at a cost of hundreds of dollars, Brevis processes them off chain at a fraction of the price. You only pay a small gas fee to verify the final result. Especially with Co Chain mode, costs are further optimized as the system does not need to generate expensive ZK Proofs for every single transaction.
What specifically can I build with Brevis right now? A: You can build unprecedented Data driven DeFi and SocialFi applications. Examples include DEXs that automatically discount fees for users meeting lifetime VIP volume standards, Lending protocols offering preferential interest rates to wallets with good credit history over the past 3 years, or on chain games dropping rare items based on a player’s past NFT ownership behavior.
The post What is Brevis? Unlocking the Blockchain Black Box with Infinite ZK Compute appeared first on NFT Evening.
Read MoreBy: Zander Brown
Title: What is Brevis? Unlocking the Blockchain Black Box with Infinite ZK Compute
Sourced From: nftevening.com/what-is-brevis/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=what-is-brevis
Published Date: Tue, 13 Jan 2026 05:02:44 +0000
----------------------------
.png)





